Chemistry 2017 JAMB Past Questions
Chemistry 2017 JAMB Past Questions
1. The general formula of alkanones is
- A. RCHO
- B. RCOR'
- C. RCOOH
- D. RCOOR
2.The constituent common to duralumin and alnico is
- A. Co
- B. Mn
- C. Al
- D. Mg
Explanation
Constituents of duralumin are: Al, Cu, Mg, Mn.Constituents of Alnico are: Al, Ni and Co
In 1909, the alloy of duralumin was discovered by Alfred Wilon consisting of 94% Al, 4% Cu, 1% Mg and 1% Mn(Manganese)
Alnico is an acronym referring to a family of iron alloys which in addition to iron are composed primarily of Al, Ni and Co.
3.The shape of the S-orbital is
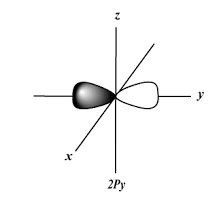 The shape of the S-orbital is spherical.
The shape of the S-orbital is spherical.
- A. elliptical
- B. spiral
- C. circular
- D. spherical
Explanation
4.Aluminium hydroxide is used in the dyeing industry as a
- A. dye
- B. dispersant
- C. salt
- D. mordant
5.The tincture of iodine means iodine dissolved in
- A. ethanol
- B. bromine chloride
- C. chlorine water
- D. water
Explanation
It is also called weak iodine solution. Tincture solutions are characterized by the presence of alcohol.
6.Temporary hard water is formed when rain water containing dissolved carbon(IV) oxide flows over deposits of
- A. CaCO3
- B. Na2CO3
- C. Na2SO4
- D. CaSO4
Correct Answer: Option A
Temporary hardness in water= Mg & Ca Carbonate.
Temporary hardness of water is caused by Magnesium and calcium hydrogencarbonate. It is formed when rainwater containing dissolved CO2 flows over deposit of CaCO3
i.e CaCO3 + CO2 + H2O → Ca(HCO3)2
Explanation
Permanent hardness in water= Mg & Ca Sulphate.Temporary hardness in water= Mg & Ca Carbonate.
Temporary hardness of water is caused by Magnesium and calcium hydrogencarbonate. It is formed when rainwater containing dissolved CO2 flows over deposit of CaCO3
i.e CaCO3 + CO2 + H2O → Ca(HCO3)2
7.The acid anhydride that will produce weak acid in water is
- A. SO3
- B. NO2
- C. SO2
- D. CO2
Correct Answer: Option D
CO2 combines with water to give a weak trioxocarbonate (IV) acid.
CO2 + H2O → H2CO3
Explanation
H2CO3 is an example of a weak acid while H2SO4 and HNO3 are examples of a strong acid.CO2 combines with water to give a weak trioxocarbonate (IV) acid.
CO2 + H2O → H2CO3
8.The process that occurs when two equivalent forms of a compound are in equilibrium is
Isomerism involves two or more forms of an element.
Reforming involves the rearrangement of molecule.
This deals with a two forms of a molecule where the chemical connectivity is the same but the electrons are distributed differently around the structure.
- A. Isotopy
- B. Resonance
- C. Isomerism
- D. Reforming
Explanation
Resonance involves two forms of a compound.Isomerism involves two or more forms of an element.
Reforming involves the rearrangement of molecule.
This deals with a two forms of a molecule where the chemical connectivity is the same but the electrons are distributed differently around the structure.
9.In the laboratory preparation of ethyl ethanoate, the water present in the mixture is removed using a solution of
- A. an hydrous CaCl4
- B. concentrated NaCO4
- C. dilute NaOH
- D. concentrated H2SO4
10.The constituent of air necessary in the rusting process are
- A. O2 and H2O
- B. Ar and CO2
- C. CO2 and H2O
- D. O2 and CO2
Correct Answer: Option A
C.
D.
=
= 2 x
T2= 600k
2–methyl butane
No of carbon=5
No of hydrogen=12
Explanation
Rust is an iron oxide, a usually red oxide formed by the redox reaction of iron and oxygen in the presence of water or air moisture.
11.For a general equation of the nature xP + yQ → mR + nS, the expression for the equilibrium constant is
- A. k [P]x [Q]y
- B.
Correct Answer: Option C
k =
Explanation
Expression for equilibrium constantk =
12. A given mass of gas occupies 2dm3 at 300k. At what temperature will its volume be doubled, keeping the pressure constant?
- A. 400k
- B. 480k
- C. 550k
- D. 600k
Explanation
At constant pressure connotes Charle's law=
= 2 x
T2= 600k
13.The oxidation number of iodine in KIO3 is
- A. +7
- B. +3
- C. +5
- D. +6
Explanation
If the rules are followed, it is non-negotiable that +5 is the suitable answer to the question.
14. An isomer of C5H12 is
- A. 2–ethyl butane
- B. butane
- C. 2–methyl butane
- D. 2–methyl propane
Explanation
C5H12 has 5 carbons acid 12 hydrogens.2–methyl butane
No of carbon=5
No of hydrogen=12
15.When few drops
of concentrated trioxonitrate(V) acid is added to an unknown sample and
wanned an intense yellow colouration is observed. The likely functional
group present in the sample is
- A. NH3—C—C=O
- B. CHO
- C. CO
-
D.
CNH2
Correct Answer: Option A
Explanation
Xanthopreitic test for the presence of protein, when conc nitric acid is added to the drop, an intense yellow colouration is observed.
It contains all the functional group of protein which includes the amino, alkanol and the carboxylic group. Adding few drops of conc HNO3 to a protein, gives an intense yellow colouration.
It is called Xanthopreitic test
16. A sample of orange juice is found to have a PH of 3.80. What is the concentration of the hydroxide ion in the juice?
- A. 1.6 10-4
- B. 6.3 10-11
- C. 6.3 10-4
- D. 1.6 10-11
- A. CH3COOH
- B. CH3COCH3
- C. CH3CH2OCH2CH3
- D. CH2CHO
- A. A saturated solution
- B. an acidic solution
- C. a buffer solution
- D. an alkaline solution
- A. low pressures and lower temperatures
- B. low temperatures and high pressures
- C. high pressures and high temperatures
- D. low pressure and high temperatures
- A. endothermic
- B. exothermic
- C. reversible
- D. ionic
- A. 226
- B. 220
- C. 227
- D. 222
- A. trigonal planar
- B. octahedral
- C. square planar
- D. tetrahedral
- A. 54.0g
- B. 27.0g
- C. 13.5g
- D. 108.0g
- A. Low melting point
- B. Weak electropositive character
- C. High boiling point
- D. White lustrous appearance
- A. 0.05
- B. 10.80
- C. 10.00
- D. 0.10
- A. oxidation reaction
- B. addition reaction
- C. hydrogenation reaction
- D. substitution reaction
- A. amylase
- B. diastatse
- C. invertase
- D. zymase
- A. CnH2n
- B. CnH2n − 2
- C. CnH2n + 1
- D. CnH2n + 2
- A. 0 to + 2
- B. 0 to + 1
- C. C + 1 to 0
- D. + 2 to + 1
- A. SO3
- B. SO2
- C. S
- D. H2S
- A. fused CaO
- B. H2O
- C. NaOH
- D. Concentrated H2SO4
- A. 0.300g
- B. 0.250g
- C. 0.2242g
- D. 0.448g
- A. 3-methybut-3-ene
- B. 2-methylbut-1-ene
- C. 2-ethylprop-1-ene
- D. 2-methylbut-2-ene
- A. Fe3 + (H2O)6
- B. FeO.H2O
- C. Fe2O3.3H2O
- D. Fe3O4.2H22O
- A. 0.1
- B. 0.5
- C. 2.0
- D. 4.0
- A. sp2 hybridized
- B. sp3 hybridized
- C. sp4 hybridized
- D. sp hybridized
- A. −100°c
- B. −273°c
- C. −373°c
- D. 0°c
- A. 20
- B. 32
- C. 14
- D. 12
- A. chlorine
- B. sulphur (IV) oxide
- C. carbon (IV) oxide
- D. ammonia
- A. further heating
- B. adding concentrated H2SO4
- C. cooling the acid solution with cold water
- D. bubbling air through the acid solution
- A. positive ion
- B. neutral atom of a metal
- C. neutral atom of a non-metal
- D. negative ion
- A. Reforming
- B. Polymerization
- C. Distillation
- D. Cracking
- A. 2.536
- B. 1.623
- C. 4.736
- D. 0.394
- A. 10.0s
- B. 12.5s
- C. 17.7s
- D. 32.0s
- A. water
- B. mercury
- C. paraffin
- D. phenol
- A. calcium hydrogentrioxocarbonate (IV)
- B. calcium trioxocarbonate (IV)
- C. calcium tetraoxosulphate (VI)
- D. calcium hydroxide
- A. bad colour
- B. bacteria
- C. temporary hardness
- D. permanent hardness
- A. NO2
- B. NH3
- C. N2O
- D. NO2
- A. negative
- B. zero
- C. positive
- D. indeterminate
Correct Answer: Option B
PH + POH =14
POH = 14 - 3.8
POH = 10.2
POH = - Log[ OH- ]
10.2 = - Log[ OH- ]
10-10.2 = [ OH- ]
[ OH- ] = 6.3 x 10-11
Explanation
PH = - Log[ H+ ]PH + POH =14
POH = 14 - 3.8
POH = 10.2
POH = - Log[ OH- ]
10.2 = - Log[ OH- ]
10-10.2 = [ OH- ]
[ OH- ] = 6.3 x 10-11
17. Incomplete oxidation of ethanol yields
Ethanol.....oxidation Ethanal........Ethanoic Acid
Primary alcohol oxidises to aldehyde and later to carboxylic acid.
Secondary alcohol oxidises to ketones.
Ethanol is an example of primary alcohol and primary alcohol can be oxidised to aldehyde and carboxylic acid. Wherein, incomplete oxidation of primary alcohol yields aldehyde also known as alkanal while complete oxidation of primary alcohol yields carboxylic acid.
Correct Answer: Option D
Explanation
C2H5OH → CH3CHO → CH3COOHEthanol.....oxidation Ethanal........Ethanoic Acid
Primary alcohol oxidises to aldehyde and later to carboxylic acid.
Secondary alcohol oxidises to ketones.
Ethanol is an example of primary alcohol and primary alcohol can be oxidised to aldehyde and carboxylic acid. Wherein, incomplete oxidation of primary alcohol yields aldehyde also known as alkanal while complete oxidation of primary alcohol yields carboxylic acid.
18. The salt formed from a weak acid and a strong base hydrolyzes in water to form
Correct Answer: Option D
Explanation
This is a solution formed from the hydrolyses of an alkali in water.
19. The ideal gas laws and equations are true for all gases at
Correct Answer: Option D
i.e, [P + ] [v - b] = RT is reduced to PV = nRT
Generally, a gas behaves more like an ideal gas at higher temperature and lower pressure as the potential energy due to intermolecular forces, it becomes less significant compared with the particles kinetic energy and the size of the molecules, then it becomes less significant compared to the empty space between them.
Explanation
At high temperature and low pressure, the vanderwaal equation is reduced to ideal gas equation.i.e, [P + ] [v - b] = RT is reduced to PV = nRT
Generally, a gas behaves more like an ideal gas at higher temperature and lower pressure as the potential energy due to intermolecular forces, it becomes less significant compared with the particles kinetic energy and the size of the molecules, then it becomes less significant compared to the empty space between them.
20.When ΔH is negative, a reaction is said to be
Correct Answer: Option B
Explanation
When ΔH is negative, heat is liberated to the surrounding and it connotes an exothermic reaction.ΔH = −ve
21
→ + alpha particle
Correct Answer: Option D
= alpha particle
considering the summation of the mass number
226 = x + 4
x = 226 - 4
x = 222
Explanation
→ += alpha particle
considering the summation of the mass number
226 = x + 4
x = 226 - 4
x = 222
22. The shape of ammonia molecules is
Correct Answer: Option A
It has three bonds of hydrogen to the Nitrogen.
Explanation
Ammonia = NH3It has three bonds of hydrogen to the Nitrogen.
23. The mass of
silver deposited when a current of 10A is passed through a solution of
silver salt for 4830s is – (Ag = 108 F = 96500(mol-1)
Correct Answer: Option A
Explanation
Recall thatmass deposited =
Mm =108, t = 4830s
I = 10A, n = 1
m = 108 × 10 × () × 1
m = 54.0g
24.Tin is unaffected by air at ordinary temperature due to its
Correct Answer: Option A
Tin is relatively unaffected by both water and oxygen at room temperature due to its low melting point. It does not rust, corrode, or react in any other way. This explains one of its major uses: as a coating to protect other metals.
Explanation
Tin has a melting point of 232° which enables it to be unaffected by air at ordinary temperature coupled with the fact that it also helps in making a good metal for alloying.Tin is relatively unaffected by both water and oxygen at room temperature due to its low melting point. It does not rust, corrode, or react in any other way. This explains one of its major uses: as a coating to protect other metals.
25.Calculate the
amount in moles of silver deposited when 9650C of electricty is passed
through a solution of silver salt [= 96500 Cmol-1]
Correct Answer: Option D
Explanation
m =where Q = IT
M = Mm ×
where m = mass
Mm = Molar mass
Q = Quantity of electricity
n = number of change= +1
= mole =
=
= × 1
= = 0.1mol
26.The reaction of halogens with alkanes in the presence of sunlight is an example of
Correct Answer: Option D
Reaction of halogen with alkane in the presence of sunlight (ultraviolet) is termed halogenation. Halogenation is an example of substitution reaction. In addition, alkanes only undergo substitution reaction but not addition reaction
Explanation
Alkanes undergoes substitution reaction and it is an example of halogenation substitution reaction.Reaction of halogen with alkane in the presence of sunlight (ultraviolet) is termed halogenation. Halogenation is an example of substitution reaction. In addition, alkanes only undergo substitution reaction but not addition reaction
27.The enzyme used in the hydrolysis of starch to dextrin and maltose is
Correct Answer: Option B
Explanation
This is any amylase or a mixture of amylases that converts starch to dextrin and maltose.
28. The alkyl group is represented by the general formula
Correct Answer: Option C
Explanation
Alkyl group has the general formula CnH2n + 1.This formed when one hydrogen is removed from the alkane family. It has the general formula CnH2n + 1
29.Cu2S(g) + O2(g) → 2Cu + SO2(g)
What is the change in the oxidation number of copper in the reaction?
Correct Answer: Option C
Explanation
In the reactant;Cu2S
2 Cu - 2(1) = 0
2 Cu = 2
Cu =
Cu = +1
In the product, Cu
Cu = O
The oxidation number of Cu in Cu2S and Cu respectively is +1 and 0 respectively
30

In the diagram above. X is
Correct Answer: Option B
Explanation
The setup represents the production of sulfur dioxide. And the cylinder marked X is SO2
31

The diagram above. Y is
Correct Answer: Option D
The setup represents the production of sulphur dioxide
Explanation
In the preparation of sulphur dioxide by the action of dilute acids on sulphates and bisulphites. conc H2SO4 helps to release SO2 from the mixture.The setup represents the production of sulphur dioxide
32.Calculate the
mass of copper deposited when a current of 0.5 ampere was passed through
a solution of copper(II) chloride for 45 minutes in an electrolytic
cell. [Cu = 64, F = 96500Cmol-1]
Correct Answer: Option D
Explanation
M ==
Copper II Chloride = CuCl2
CuCl2 → Cu2+ + 2Cl2
Mass of compound deposited =
Q = IT
I = 0.5A
T = 45 × 60
T = 2700s
Q = 0.5 × 2700
= 1350c
Molarmass = 64gmol-1
no of charge = + 2
Mass =
Mass = 0.448g
33.C3H5 - COH3 =CH2
The IUPAC nomenclature of the structure above is
Correct Answer: Option B
Start the numbering from the terminal carbon.
Explanation
CH2CH2 - CCH3CH2Start the numbering from the terminal carbon.
34.The reddish–brown rust on ion roofing sheets consists of
Correct Answer: Option C
4Fe + 3O2 → 2 Fe2O2
Fe2O3 + H2O → Fe2O3.H2O
Explanation
Iron [Fe] reacts with H2 in the presence of oxygen to form a rust.4Fe + 3O2 → 2 Fe2O2
Fe2O3 + H2O → Fe2O3.H2O
35. The densities of two gases, X and Y are 0.5gdm-3 and 2.0gdm-3 respectively. What is the rate of diffusion of X relative to Y?
Correct Answer: Option C
Explanation
The rate of dimension of a gas inversely proportional to the square root of its molecular mass or its density, which is Graham's Law of diffusion of gas.R ∝ or R ∝
Dx = 0.5gdm-3, Dy = 2gdm-3
R=
R = k
R1 = R1
Rx = Ry
=
=
= 2.0
36. The carbon atoms on ethane are
Correct Answer: Option B
Explanation
Alkane's family are sp3 hybridized
37. According to Charle's law, the volume of a gas becomes zero at
Correct Answer: Option B
i.e −273°c + 273 = OK
At zero kelvin, the volume of a gas becomes zero
Explanation
Where −273°c = OKi.e −273°c + 273 = OK
At zero kelvin, the volume of a gas becomes zero
38. An oxide XO2 has a vapour density of 32. What is the atomic mass of X?
Correct Answer: Option B
Explanation
Molecular mass = vapour density X2Mm of XO2 = x + 16(2) = x + 32
vapour density = 32
∴ x + 32 = 32 × 2
x + 32 = 64
x = 64 - 32
x = 32
∴ the relative molecular mass of X is 32
Relative molecular mass = vapour density × 2
39.The gas that can be collected by downward displacement of air is
Correct Answer: Option D
 Upward delivery works well for hydrogen and ammonia, which are
both less densed than air. Sometimes, they are collected over water.
Upward delivery works well for hydrogen and ammonia, which are
both less densed than air. Sometimes, they are collected over water.
Explanation
40. In the laboratory preparation of trioxonitrate (V) acid the nitrogen(iv) oxide formed as a by-product is removed by
Correct Answer: Option D
Explanation
Bubbling of air through the acid solution removes deposited oxides of nitrogen.Nitric acid is prepared in the laboratory by heating a nitrate salt with the concentrated acid.
NaNO3 + H2SO4 → NaHSO4 + HNO3
Vapours of nitric acid are condensed to a brown liquid in a receiver cooled under cold water. "Dissolved oxides of nitrogen" e.g NO2 are removed by redistillation or blowing a current of carbondioxide or dry air through the warm acid
41.A particle that contains 9 protons, 10 neutrons and 10 electrons is
Correct Answer: Option D
neutrons = 10
electrons = 10
Electronic configuration = 2, 8
Ground state Electronic configuration=2, 7
It means that the atom has gained an electron thereby making it have a negative ion.
When an atom donates an electron, it becomes positively charged.
When an atom accepts an electron, it becomes negatively charged
Explanation
protons = 9neutrons = 10
electrons = 10
Electronic configuration = 2, 8
Ground state Electronic configuration=2, 7
It means that the atom has gained an electron thereby making it have a negative ion.
When an atom donates an electron, it becomes positively charged.
When an atom accepts an electron, it becomes negatively charged
42. Ethene is prepared industrially by
Correct Answer: Option D
Explanation
Ethene is produced from cracking which involves breaking up large hydrocarbon molecules into smaller and more useful bits. This is achieved by using high temperatures and pressures without a catalyst.C15H32 → 2C2H4 + C3H6 + C8H14
......Δheat...ethene........propene.........octane
43. Calculate the amount in moles of a gas which occupies 10.5 dm3 at 6 atm and 30oC [R = 082 atm dm3 K-1 mol-1]
Correct Answer: Option A
Explanation
For an ideal gas PV = nRTAmount in moles = n
Volume v = 10.5dm3
Pressure P = 6atm
Temperature T = 30°C + 273 = 303k
R, Gas constant = 0.082 atmdm3k-1 mol
Recall from ideal gas equation
pv = nRT
n =
n =
n= 2.536mol
44. If 100cm3
of oxygen pass through a porous plug is 50 seconds, the time taken for
the same volume of hydrogen to pass through the same porous plug is? [O =
16, H = 1]
Correct Answer: Option B
Explanation
Rate of diffusion orRate =
or
Time or
At constant volume of 100cm3
=
=
tn2= 12.5s
45. Due to the high reactivity of sodium, it is usually stored under
Correct Answer: Option C
Explanation
Na is kept under kerosene (paraffin) to avoid reactivity with air.Paraffin is also known as Kerosene.
Na(sodium) is kept in kerosene to prevent it from coming in contact with oxygen and moisture. If this happens, it will react with the moisture present in air and form sodium hydroxide.
46. The furring of kettles is caused by the presence in water of
Correct Answer: Option B
CaCO3 causes the furring of kettles
Explanation
Furring of kettles is caused by the temporary hardness in water. Temporary hardness in water is caused by calcium and magnesium trioxocarbonate (IV)CaCO3 causes the furring of kettles
47. Water for town supply is chlorinate to make it free from
Correct Answer: Option B
Explanation
Chlorine helps to keep water from germs and bacteria.
48.Ca(OH)2(s) + 2NH4Cl(g) → CaCl2(s) + 2H2O2(l) + X. In the reaction above X is
Correct Answer: Option B
Ca[OH]2 + 2NH4Cl → CaCl2 + 2H2O + 2NH3
X = NH3
Explanation
Balancing the chemical equation.Ca[OH]2 + 2NH4Cl → CaCl2 + 2H2O + 2NH3
X = NH3
49. X(g) + 3Y(g) ---- 2z(g) H = +ve. if the reaction above takes place at room temperature, the G will be
Correct Answer: Option D
Explanation
ΔG= ΔH − TΔS.
To determine whether ΔG will be positive or negative, the value of ΔH(change in enthalpy) and ΔS (change in entropy) must be given. Likewise the temperature.



Comments
Post a Comment